 How
to subtract background?
How
to subtract background?
 How
to measure and save fluorescence intensity values using ROIs?
How
to measure and save fluorescence intensity values using ROIs?
 How
to run Image Stabilizer (register or align images)
How
to run Image Stabilizer (register or align images)
-
Select the Editing/ Align
Series (Image Stabilizer) function in the Editing
menu
Align
Series (Image Stabilizer) function in the Editing
menu
-
Select the best signal to noise ratio channel as
Image (A) by checkmarking in the left list in the center of the
parameter bar
-
Select all images as
Image (B) by
checkmarking in the right list in the center of the
parameter bar
-
The image registration is ready run now by
pressing the  button
button
More on this topic:
 How
to create and use Reference Images?
How
to create and use Reference Images?
- Mark any image as reference image by right-click/Set as Reference
Image. Alternatively use the I/O/
 Set
Reference Image function
Set
Reference Image function
- An image can by any of these three reference image
types: Background / Dark Current, Blank for OD /
Normalization, Histogram
- Reference images are not closed by Close All,
use File/Close All Reference Images to close them
- Use reference images in the following functions:
 How
to run a pipeline?
How
to run a pipeline?
- Select a pipeline in the Pipelines menu, or open a pipeline file (*.ips)
by drag-and-dropping on the main workplace, or by opening a new Pipeline
Window in the PipelineDesigner menu
- If you have open images, use any of these alternatives:
- Press
 button in the main toolbar to run the pipeline in the top
window. This is equivalent to the same button in the Pipeline
Window.
button in the main toolbar to run the pipeline in the top
window. This is equivalent to the same button in the Pipeline
Window.
- Right-click the image and use
 Process this
Process this
- Select a single image to as
Image (A) in the the window press the
 toolbar
button
toolbar
button
- If you have an open Multi-Dimensional Open
dialog, use the
 button in the main toolbar, in the dialog or in the Pipeline Window
to load recording and subsequently process with the pipeline
button in the main toolbar, in the dialog or in the Pipeline Window
to load recording and subsequently process with the pipeline
- The
 button also serves automation, select Run Pipeline in All
Stage Positions to evaluate the whole recording
button also serves automation, select Run Pipeline in All
Stage Positions to evaluate the whole recording
 How
to work with XYZT recordings (time lapse of z-stacks)?
How
to work with XYZT recordings (time lapse of z-stacks)?
Image Windows can contain only 2D time lapses. However analysis of XYZT
stacks is supported by z-projection during reading the data set. Control the
projection in the Settings tab of the dialog. Use Mean intensity projection,
and projection of sub-stacks (Load specified frames only... and Use z-drift
stabilizer checkboxes) if mesuring intensities in XYZT recordings.
 How
to work with recordings from multiwell plates?
How
to work with recordings from multiwell plates?
- Opening a single multi-dimensional data file (such as *.nd2, *.nd,
*.lif, *_Sum.lsm) results a Multi-Dimensional Open
dialog.
- Select the actual well in the top of the Open tab and press
Open to load images. Use the Close All Before checkbox and the
Open Next button to walk through the recording
- Optionally rename wells using the Plate tab, or
individually using the pencil button.
- Use the drop-down menu of the
 button to automate multiwell / multiple stage position data
analysis
button to automate multiwell / multiple stage position data
analysis
- Optionally, walk through the data set using the
 button set to Clear and Run Next Stage Position, and using a
visualization pipeline, such as
button set to Clear and Run Next Stage Position, and using a
visualization pipeline, such as
 Show three color overlay.
Show three color overlay.
- If the data is arranged as one file per stage position,
use multiple selection during opening or drag-and-dropping,
and set the File merge box
to Merge as Positions in the Open tab
of the Multi-Dimensional Open
dialog.
 When
to use the internal loader and when Bio-Formats?
When
to use the internal loader and when Bio-Formats?
- The internal loader has limited format compatibility (TIFF, LSM,
STK, ND2, INF files), but is substantially faster than using
Bio-formats. Time stamps are correctly read. Not all features of the
Multi-Dimensional Open dialog are
available for each format.
- The Bio-formats reader is compatible with a large array of
biological formats, but is slower than the internal reader, All
functions of the Multi-Dimensional Open
dialog are supported. The time stamps may be wrongly read for certain
formats.
To switch between Internal loader and Bio-formats:
- Use the File type filter of the Open dialog
- File/Set Folder Locations and Default Open Method menu
point
- Note: Drag-and-drop open method follows the last Fie
type filter or Default Open Method settings, but if an
unrecognizable file is dropped on the workplace, it will
automatically switch to Bio-formats.
 How
to scale image intensities identically for comparison?
How
to scale image intensities identically for comparison?
- Select the Appearance/
 Set
Scaling/LUT function
Set
Scaling/LUT function
- Set Scale type to Fixed Value
- Enter Min Value and Max Value
- Either select images to scale as image (A) and press
the
 button
button
- Or right-click each image and select the
 Process This menu point.
Process This menu point.
 How
to transfer images to a presentation software?
How
to transfer images to a presentation software?
- Right-click the Image Window and select Copy Image or Copy Image with all
ROIs
- Right-click the scale bar in the status bar of the Image
Window and select Copy Scalebar to Clipboard
- Right-click the Image Window and select Copy Plot Image
- Use the File/Export... menu points or the I/O/
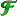 Export
function.
Export
function.
 How
to overlay images?
How
to overlay images?
Right-click the Image Window and select Attach Overlay Image.
 How
to segment an image (series) showing fluorescent cells or nuclei?
How
to segment an image (series) showing fluorescent cells or nuclei?
 How
to count cells in view fields, whole wells or whole microplates?
How
to count cells in view fields, whole wells or whole microplates?
 How
to measure rates of change of fluorescence intensity?
How
to measure rates of change of fluorescence intensity?
 How
to calculate fluorescence ratio?
How
to calculate fluorescence ratio?
The best way to calculate fluorescence ratios is dividing mean fluorescence
intensities measured in ROIs. To perform this with a single command, use the Plotting/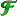 Plot
Ratio function. Select the numerator and denominator as
Image (A) and (B),
respectively.
Plot
Ratio function. Select the numerator and denominator as
Image (A) and (B),
respectively.
To calculate a ratio image, use the Math/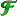 Ratio
function. Select the numerator and denominator as
Image (A) and (B),
respectively. Note that you can measure ROI means of ratios in the ratio image,
but results will be a lot noisier than using the Plotting/
Ratio
function. Select the numerator and denominator as
Image (A) and (B),
respectively. Note that you can measure ROI means of ratios in the ratio image,
but results will be a lot noisier than using the Plotting/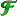 Plot
Ratio function.
Plot
Ratio function.
 How
to apply high pass filtering to selectively measure mitochondrial fluorescence?
How
to apply high pass filtering to selectively measure mitochondrial fluorescence?
The originally published high pass filter (Cell
Calcium. 30.5:311-321) is applicable to 512x512 pixels images at
0.15-0.2 µm resolution:
- To use this original filter, select the Filters/
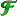 2D
DFT Filter, and as Filter file locate
\Image Analyst\Filters\the original X-rhod-1 mito
filter.flt in the Documents folder.
2D
DFT Filter, and as Filter file locate
\Image Analyst\Filters\the original X-rhod-1 mito
filter.flt in the Documents folder.
- Set Absolute to Yes.
- If the recorded image is 512x512 pixels, set
Preserve edges to Yes.
- If the recorded image is smaller than 512x512, set Enlarge paper to Yes, and
Preserve edges to No.
To properly use the original filter, a non-quadrangular
image has to be smaller than 512x512, and set the
Enlarge image to power of 2 to 9.
- Hint: use the Editing/
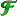 Crop
and Editing/
Crop
and Editing/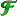 Resample
Image to match an image size and resolution to the
original filter. Alternatively design a new filter for
your recording below.
Resample
Image to match an image size and resolution to the
original filter. Alternatively design a new filter for
your recording below.
Creating and using new high pass (band pass)
filters:
- Open an image.
- To test a filter, go to Tools/Set
DFT Filter and Filter Optimizations dialog,
Generate tab and select
2D DFT Butterworth BP
Filter.
- Set Absolute to Yes.
- If the recorded image is quadrangular and sized as
power of 2 (256x256, 512x512, 1024x1024) set
Preserve edges to Yes.
- If the recorded image is not quadrangular and sized
as power of 2, set Enlarge paper to
Yes, and Preserve edges
to No. To properly use the
original filter, set the Enlarge image to
power of 2 to a value so 2^this value is larger
than the longest edge of the image.
- Enter a higher cut off and a lower cut on value and
press the preview button.
- Adjust parameters and see the results.
- To numerically optimize a high pass (band pass) filter (will come
with version 3.0.1):
- Open an image.
- To create a new filter with numerical optimization, go to Tools/Set
DFT Filter and Filter Optimizations dialog,
Optimization tab and select
High Pass, Band
Pass, Long Pass Filter. Follow this latter link
for details how to perform optimization.
- Copy the optimized Cut on and Cut off parameters to
the Filters/
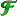 2D
DFT Butterworth BP Filter, Note that the
optimized cut on and cut off frequencies (ω)
are given in pixels, so set the Units of ω parameter to
pixels.
2D
DFT Butterworth BP Filter, Note that the
optimized cut on and cut off frequencies (ω)
are given in pixels, so set the Units of ω parameter to
pixels.
 How
to subtract background?
How
to subtract background? How
to measure and save fluorescence intensity values using ROIs?
How
to measure and save fluorescence intensity values using ROIs? How
to run Image Stabilizer (register or align images)
How
to run Image Stabilizer (register or align images)![]() Align
Series (Image Stabilizer) function in the Editing
menu
Align
Series (Image Stabilizer) function in the Editing
menu![]() button
button How
to create and use Reference Images?
How
to create and use Reference Images? How
to run a pipeline?
How
to run a pipeline? How
to work with XYZT recordings (time lapse of z-stacks)?
How
to work with XYZT recordings (time lapse of z-stacks)? How
to work with recordings from multiwell plates?
How
to work with recordings from multiwell plates? When
to use the internal loader and when Bio-Formats?
When
to use the internal loader and when Bio-Formats? How
to scale image intensities identically for comparison?
How
to scale image intensities identically for comparison? How
to transfer images to a presentation software?
How
to transfer images to a presentation software? How
to segment an image (series) showing fluorescent cells or nuclei?
How
to segment an image (series) showing fluorescent cells or nuclei? How
to count cells in view fields, whole wells or whole microplates?
How
to count cells in view fields, whole wells or whole microplates? How
to measure rates of change of fluorescence intensity?
How
to measure rates of change of fluorescence intensity? How
to calculate fluorescence ratio?
How
to calculate fluorescence ratio?![]() Plot
Ratio function. Select the numerator and denominator as
Image (A) and (B),
respectively.
Plot
Ratio function. Select the numerator and denominator as
Image (A) and (B),
respectively.![]() Ratio
function. Select the numerator and denominator as
Image (A) and (B),
respectively. Note that you can measure ROI means of ratios in the ratio image,
but results will be a lot noisier than using the Plotting/
Ratio
function. Select the numerator and denominator as
Image (A) and (B),
respectively. Note that you can measure ROI means of ratios in the ratio image,
but results will be a lot noisier than using the Plotting/![]() Plot
Ratio function.
Plot
Ratio function. How
to apply high pass filtering to selectively measure mitochondrial fluorescence?
How
to apply high pass filtering to selectively measure mitochondrial fluorescence?